2. Development of German cities using the example of the Ruhr area
Questions
Geographical/Historical Context
Congested areas, like those in Germany, whose origin, growth and fast spread date back to the times of the industrialization, emerged all over Europe. Yet, it should be taken into account that not all the regions of the country showed congested areas; Bavaria, for example, remained mainly agricultural, whereas the Ruhr district registered an enormous population shift towards urban areas.
In order to become an industrial centre, an area had to fulfil specific premises, which were the same for nearly all centres. Apart from a solid base of raw material, the connection to transport routes was of high importance. The products and goods developed and produced by large companies were transported by ship or by train, while other goods necessary for processing were imported. In the infrastructure, a large labour force who sought work in the factories had to be available.
Answer to the Questions
1:
- Urbanization as a side effect of industrialization.
- Population shift from countryside to town.
- The main phase of the industrialization after 1871 in Germany.
2:
- Urbanization of the Ruhr area: a coherent congested area.
- Raw materials (coal and iron deposit) were decisive for the growth.
- Developed infrastructure: connection to train/road world transport routes.
3: Coal and iron.

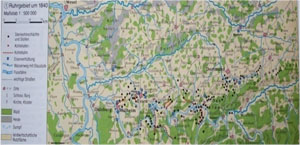
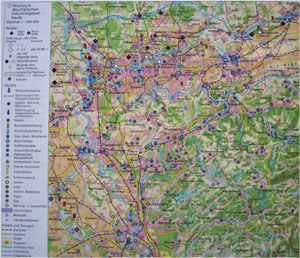



Presentation
In the course of industrialization, an enormous city growth took place due to the influx of workers. The Ruhr district in Germany has become the centre of the heavy industry in Germany due to the natural resources which are to be found there.